Information
What is LLA?
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the abnormal growth of immature cells (blasts) in the bone marrow.
These immature cells displace normal cells (red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets) causing fever, fatigue, rapid bruising, bleeding problems, infections, among other alterations. Acute leukemia usually causes symptoms to get worse over a short period of time.
What is the etiology of acute leukemias?
Its etiology is still unknown, but it is associated with risk factors such as:
✓ Predisposing genetic factors (5%).
✓ Congenital disease (10-30 times> risk): Fanconi anemia, Bloom Syndrome, Ataxia-telangiectasia, Down syndrome.
✓ Exposure to Radiation.
✓ Exposure to pesticides.
✓ Patients who are treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy for other types of cancer can develop acute leukemias
What is the incidence of ALL?
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is the most common malignant disease in the pediatric population.
ALL corresponds to 75% of oncological diseases.
The maximum peak incidence is between 2 and 5 years of age.
ALL is more common in males than females.
What are the most common signs and symptoms of ALL?
The signs and symptoms of ALL include the following:
• Frequent infections.
• Fever.
• Rapid bruising.
• Bleeding that is difficult to stop.
• Tiny, smooth, dark red spots on the skin (petechiae) due to bleeding under the skin.
• Pain in the bones or joints.
• Lumps in the neck, under the arm, in the stomach or groin.
• Pain or tightness under the rib cage.
• Feeling very tired or weak.
• Paleness
• Loss of appetite.
• Breathing Difficulties.
How is ALL diagnosed?
The specialist will perform a detailed analysis of the patient’s medical history, complete physical examination, request complete blood laboratories and specialized tests that will indicate the diagnosis of ALL.
How is ALL treated?
The main therapy or treatment for patients diagnosed with ALL is chemotherapy.
There are different treatment options, the specialist will indicate the appropriate treatment for each patient depending on the risk group.
Within the group of chemotherapeutic agents, asparaginase plays a very important role in the treatment of ALL, because it eliminates leukemic cells.
There are 3 types of asparaginase, two derived from a bacterium called E. Coli and one derived from Erwinia chrysanthemi.
When patients have allergic reactions to E. coli derived asparaginase, patients can continue their treatment with Erwinia asparaginase.
What are the benefits of using Erwinia Asparaginase?
Number 1
The incidence of life-threatening neurotoxicity, pancreatitis, and sepsis was significantly lower in children treated with Asparaginase Erwinia compared to those receiving E. coli ASP. 2.
Number 2
The physiological levels of Asparagine recover faster after the administration of ASP Erwinia vs. preparations of ASP derived from E. coli2
.
Number 3
Switching to Asparaginase Erwinia in patients with positive CA or allergy symptoms, reduced the risk of treatment failure rate from 3.2 to 0.62.
.
Number 4
Patients with silent hypersensitivity, who continue to receive asparaginase derived from E. Coli, have worse results. This shows that the presence of AC anti-asparaginase (in the absence of allergy) and subsequent switch to Erwinia ASP could mitigate the adverse effects of silent hypersensitivity 2.
Number 5
Due to the different bacterial source of ASP E. chrysanthemi, there is no cross-reactivity with antibodies generated against ASP derived from E. coli.
Number 6
Physiological levels of asparagine recover faster after the administration of ASP Erwinia vs the preparations of ASP derived from E. coli2.
Number 7
Patients who develop a hypersensitivity reaction and are switched to alternative ASP preparations produce similar clinical results to patients who did not have a hypersensitivity reaction.
Number 8
The DFS in patients who received Erwinia asparaginase at 5.4 years was higher, compared to patients who never developed hypersensitivity reactions (86.5% and 81.3%).
Number 9
The results showed that Asparaginase Erwinia Chrysanthemi was well tolerated and, more importantly, maintained asparaginase activity> 0.1 IU / ml at 48 and 72 h in all patients analyzed.
Bibliographic references:
1. Burke. M., J. How to manage asparaginase hypersensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia,
Future Oncol. (2014) 10(16), 2615–2627. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.138. PMID: 24983955.
2. Cecconello. D., K., Magalhães. M., et al. Asparaginase: an old drug with new questions, hematol
transfus cell ther. 2 0 2 0;4 2(3):275–282. doi.org/10.1016/j.htct.2019.07.010
3. Egler. R., A., Ahuja. S., P., et al. L‑asparaginase in the treatment of patients with acute
lymphoblastic leukemia, J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2016 Abr-Jun; 7(2): 62–71. doi: 10.4103 / 0976-500X.184769. PMID: 27440950; PMCID: PMC493608
4. Pieters, R.,Hunger. S.P., et al. L-asparaginase treatment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: afocus
on Erwinia asparaginase: Cancer. 2011 January 15; 117(2): 238–249. doi: 10.1002 /cncr.25489. Epub 2010 Sep 7. PMID: 20824725; PMCID: PMC3000881.
5. Plourde, P.V., et al. Safety Profile of Asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi in a Large Compassionate-Use Trial: Pediatr Blood Cancer 2014;61:1232–1238. doi: 10.1002 / pbc.24938. Epub 2014 Jan 16. PMID: 24436152.
6. Salzer, W., Bostrom. B., et al. Asparaginase activity levels and monitoring in patients with acute
lymphoblastic leukemia, Leukemia & Lymphoma, 59:8, 1797-1806, doi: 10.1080
/10428194.2017.1386305. Epub 2017 Oct 18. PMID: 29045165.

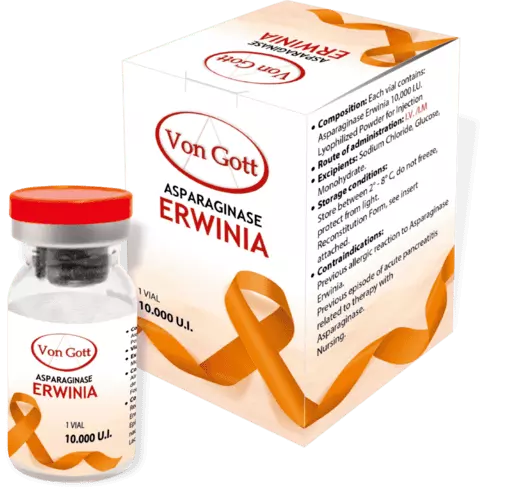
Asparaginase Erwinia
Presentation
Lyophilized Powder for reconstitution to Injectable solution.
Vial 10,000 I.U.
Route of Administration: I.V. / I.M.
Contraindications
The use of Asparaginase Erwinia is contraindicated in the following cases:
✓ In patients with severe hypersensitivity reactions to Asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi, including anaphylaxis.
✓ In patients who have presented the following adverse reactions, after treatment with Asparaginases derived from E. Coli:
Severe pancreatitis
Severe thrombosis
Serious bleeding events.
The specialist will evaluate each case and the risk or benefit of continuing or not with Asparginase therapy.


Love|Understanding|Support


Happiness|Positivism|Faith


Change|Companionship|Growth
Important
This website is entirely for informational purposes for health personnel, at no time is self-medication sought without the pre-registration of a health professional.